Causal Enhanced Autoregressive Model for Monocular Image-Goal Navigation in Unknown Map Environment
Published:
Abstract
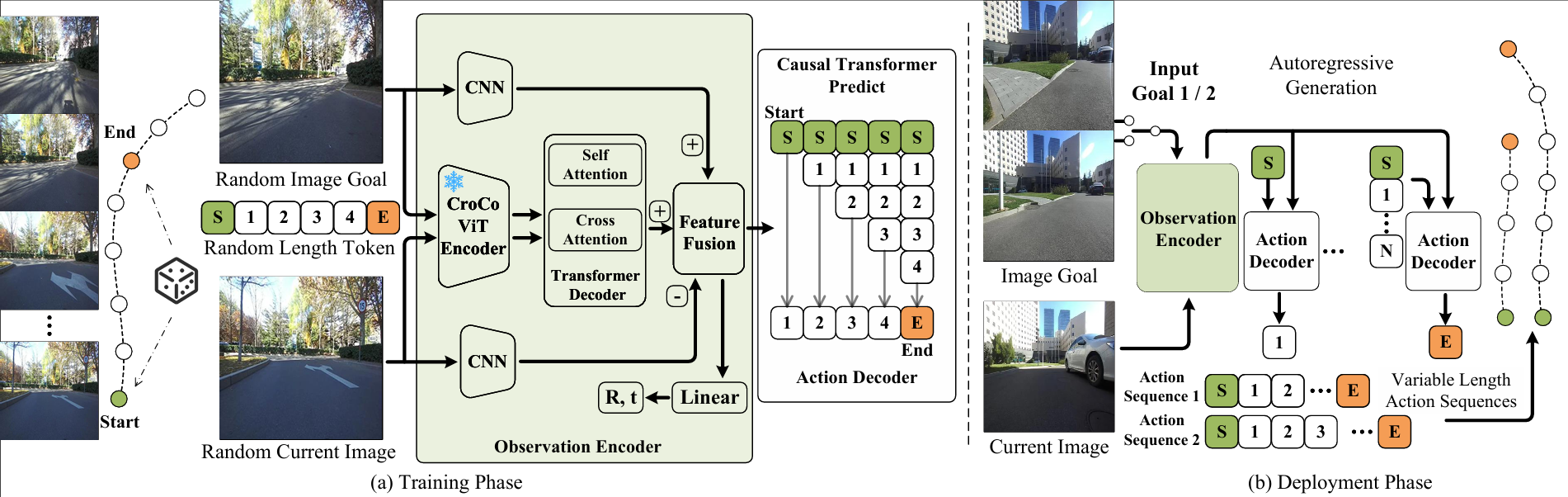
Monocular image-goal navigation in an outdoor environment is a challenging task. Robots have to face monocular scale uncertainty and complex environments. Recently, implementations based on imitation learning have made significant progress. However, robots tend to focus too much on the current state and ignore the image goal, which is the phenomenon of causal confusion. We propose an autoregressive framework called ArMoNa to address this limitation and enhance the causal relationship between the goal image and the action. In the training phase, we use a pre-trained 3D vision model to construct an observation encoder. We randomly select the current and goal images and feed them into the observation encoder to get fusion features. The autoregressive action decoder generates discrete waypoints based on fusion features. In the deployment phase, after obtaining the fusion features, we input the start token into the action decoder. The action decoder loops to predict the next waypoint until the end token appears. The variable length waypoint training of autoregression enhances the model’s attention to the goal image. We test our framework in both simulated and real environments. Compared to the most advanced methods, our model demonstrates the highest navigation success rate. In addition, our model can generalize to different camera devices such as mobile phones, demonstrating stronger robustness in visual navigation tasks.
Reference
Zengmao Wang, Hao Hu, Wei Gao*, Shuhan Shen, Causal Enhanced Autoregressive Model for Monocular Image-Goal Navigation in Unknown Map Environment. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 10(8), 8364-8371, 2025.DOI
